Newton's Third Law
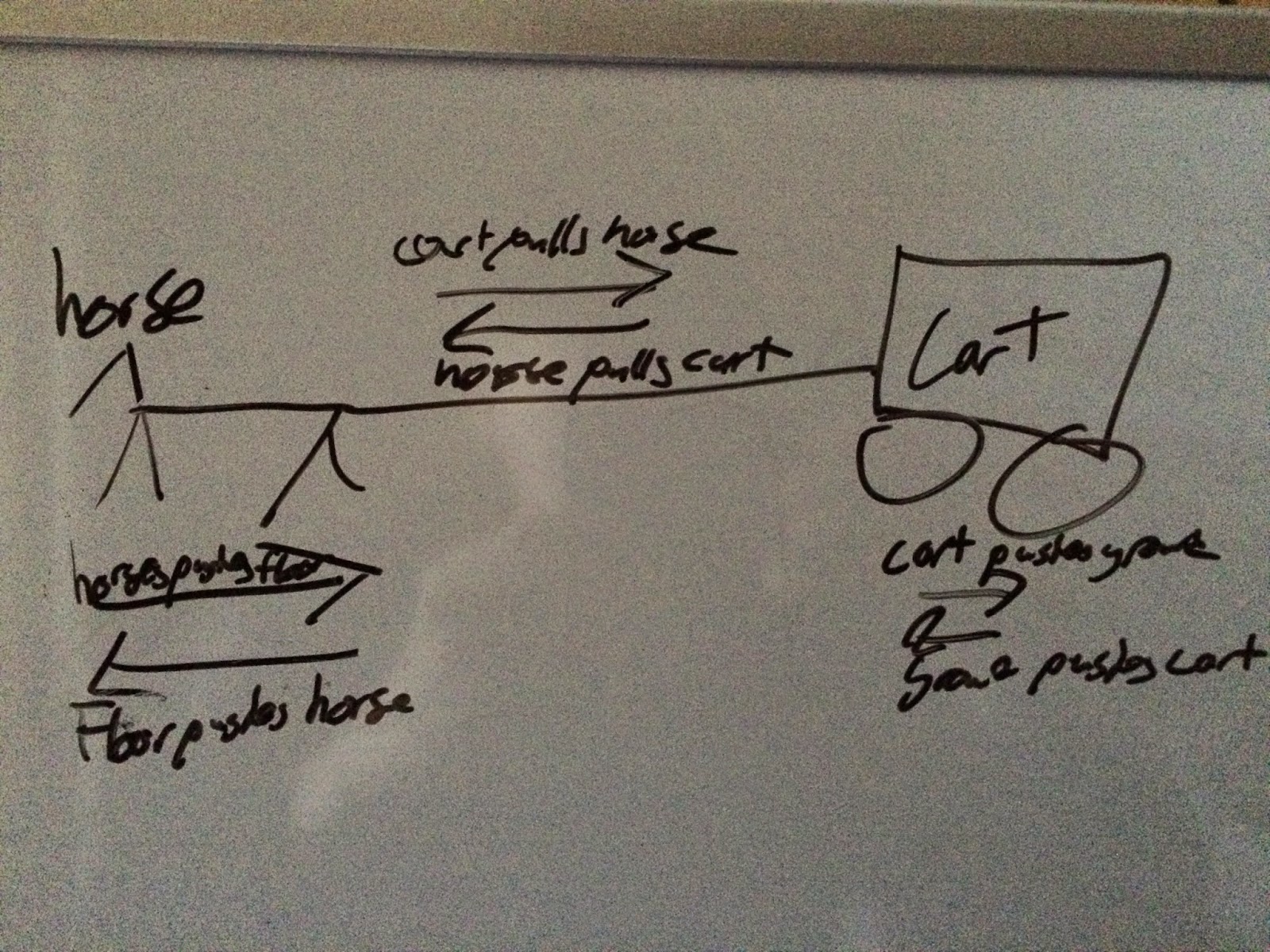
His third law states that every action caused upon an object, or is caused by an object, has an equal and opposite reaction. What does this mean? Well, when you are walking forward, you push the ground behind you; push is a type of force. This force and action has a reaction to it which is the ground pushes you forward. To have a real action and reaction pair, the force has to be the same between the same objects. In this action and reaction pair, the forces are equal, which means if you were showing a picture, the vectors will also be equal. Here is an example with a horse pulling a cart (Sorry for the bad writing):
As you can see, The vectors for the horse and ground using one another are similar to the size of the horse and cart pulling one another. This is because they're similar forces, but you see the cart and ground pushing vectors are smaller than both is because the cart isn't really causing itself to push the ground, it's being pulled by the horse, so less force itself.
Perpendicular Forces
In the above, I wrote about how parallel forces are there and now what about what happens when you are in a boat sailing to cross a river thats flowing a certain speed. Let's say the river flows 5m/s down and the wind pushes you about 3m/s. Here is an example:
Here, since the rive flows down 5m/s and you sail across 3 m/s, your boat will go at an angle 4m/s, until you hit the x. We know it's 4 because of our 3-4-5 right triangles. These forces and actions happen in everyday life such as boat in a river or a plane with wind pushing it.
Tides
In this unit, we also learned about tides. Tides happen everyday on Earth. We experience 4 tides a day, 2 high and 2 low. Each high and low tide are 6 hours apart from each other, so that means each high tide is 12 hours apart, same for low tides. What causes these tides is the force of pull from the moon. The moon pulls the water and Earth towards it, but the Earth fights back, kind of like tug of war. The formula/equation we use to show the force of gravity is F=G(m1m2/d^2). G is 7*10^24 (or near that).Since the Earth pulls back to stay in its orbital, it causes the tide bulge, which is the oval water shape. If the moon pulls the water closest to it/ the side of Earth facing it with let's say 5N, then the other water side is being pulled with -5N because of this tug of war. Negative is a force in the other direction. This means that if theres a high or low tide on one side of the earth, then it's the same on the opposite side. Tides are caused by the phases of the moon and sun. When the sun and moon line up with he earth in somewhat a straight line, those are called spring tides, when the tides are higher then usual. When the moon is on one side of the earth and the sun is on the other side, 90 degrees, this forms neap tides.
Momentum
Last thing we learned about was momentum. Momentum in physics variables is p, and p=mass(velocity) [p=mv] measured in kgm/s. We learned that when an object that's moving hits another object thats at rest, gives/passes its momentum through it and moves/sticks together and moves together at a new velocity. Same momentum? Yes, because the momentum before is equal to the momentum after. Also, if there was a change in momentum on an object, to find this change you would use the final momentum minus the initial/starting one. This leads to the impulse on objects too. Impulse is the variable J. J= the change in momentum and it also equals force times the change in time. This is measured in Ns. Law of conservation momentum is showing the relation momentum and impulse. All of this helps us figure out why gymnast use matts instead of the hard floor to land on, the matts slow them down (longer time), so small force, and small force causes less injury. This also shows us why we don't have rubber bumpers on cars, land with bent knees, and landing in snow can help us survive off a mountain.